What is MFC?
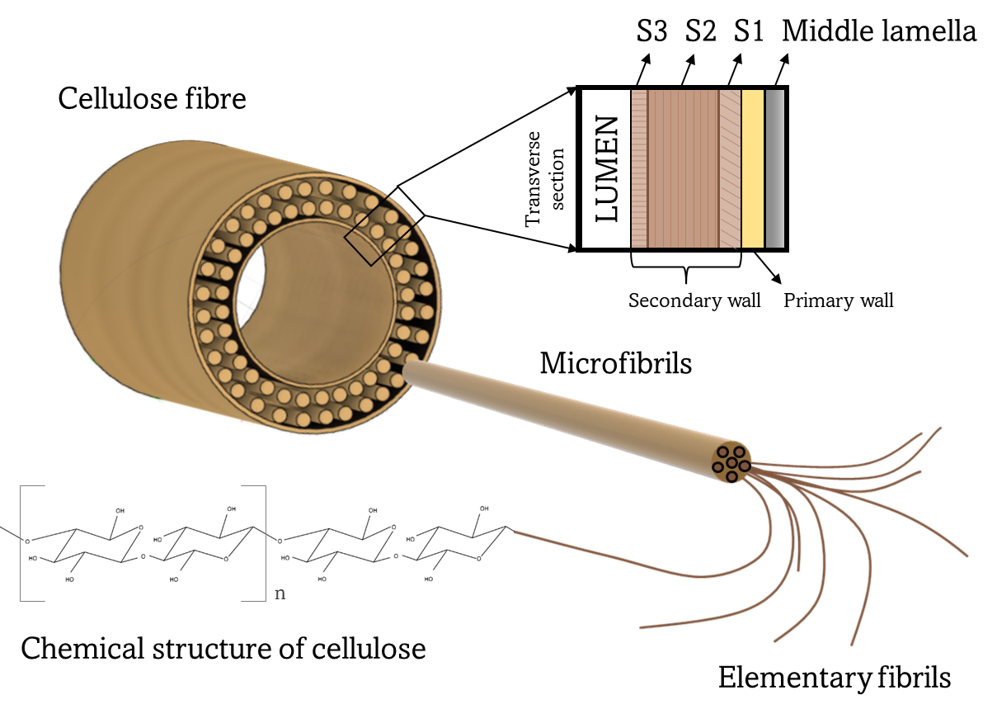
Cellulose fibres are an essential structural component in plants, and are a fundamental constituent of paper and board products. Cellulose fibres have a hierarchical microstructure consisting of fibrils and microfibrils.
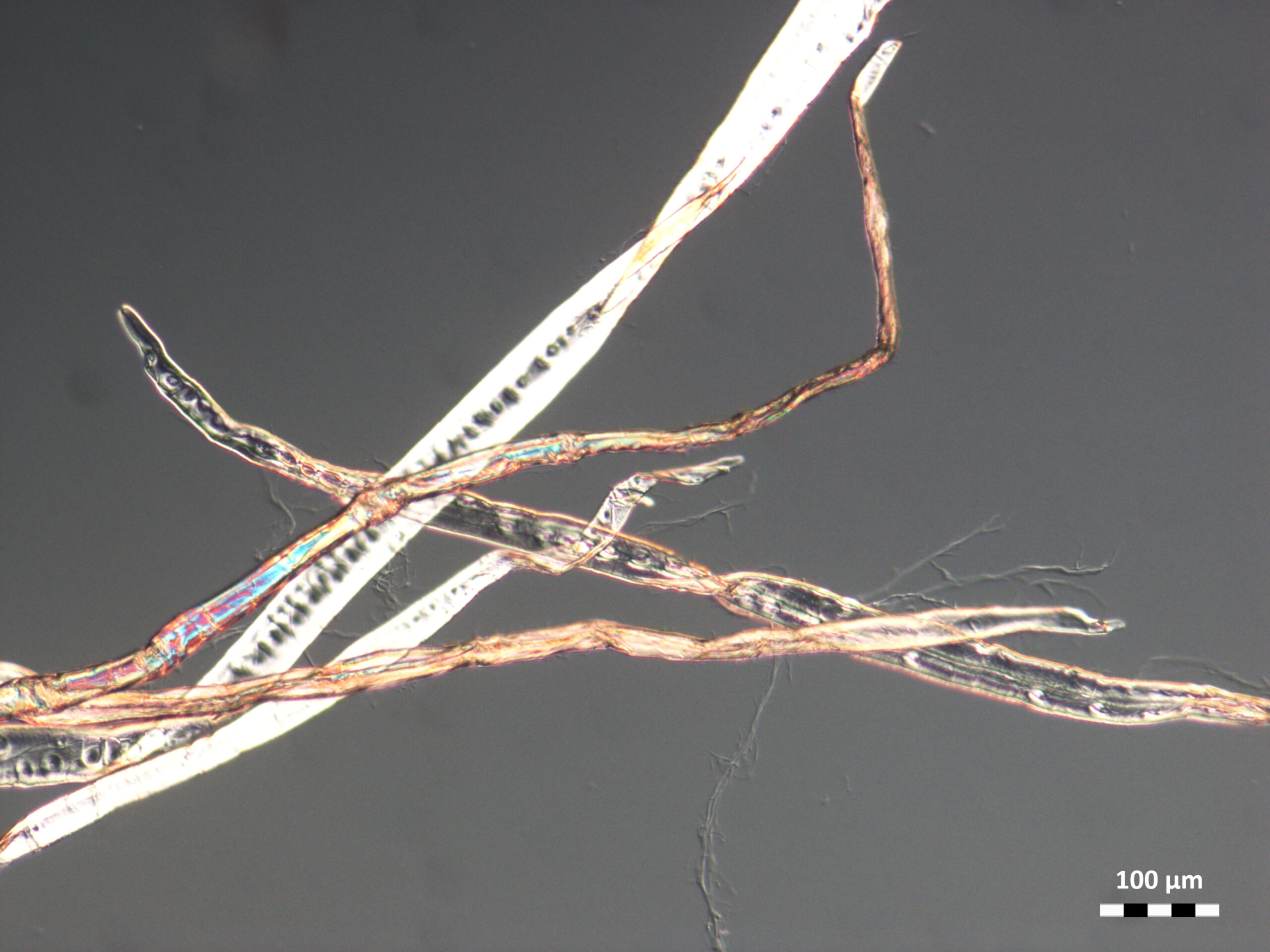
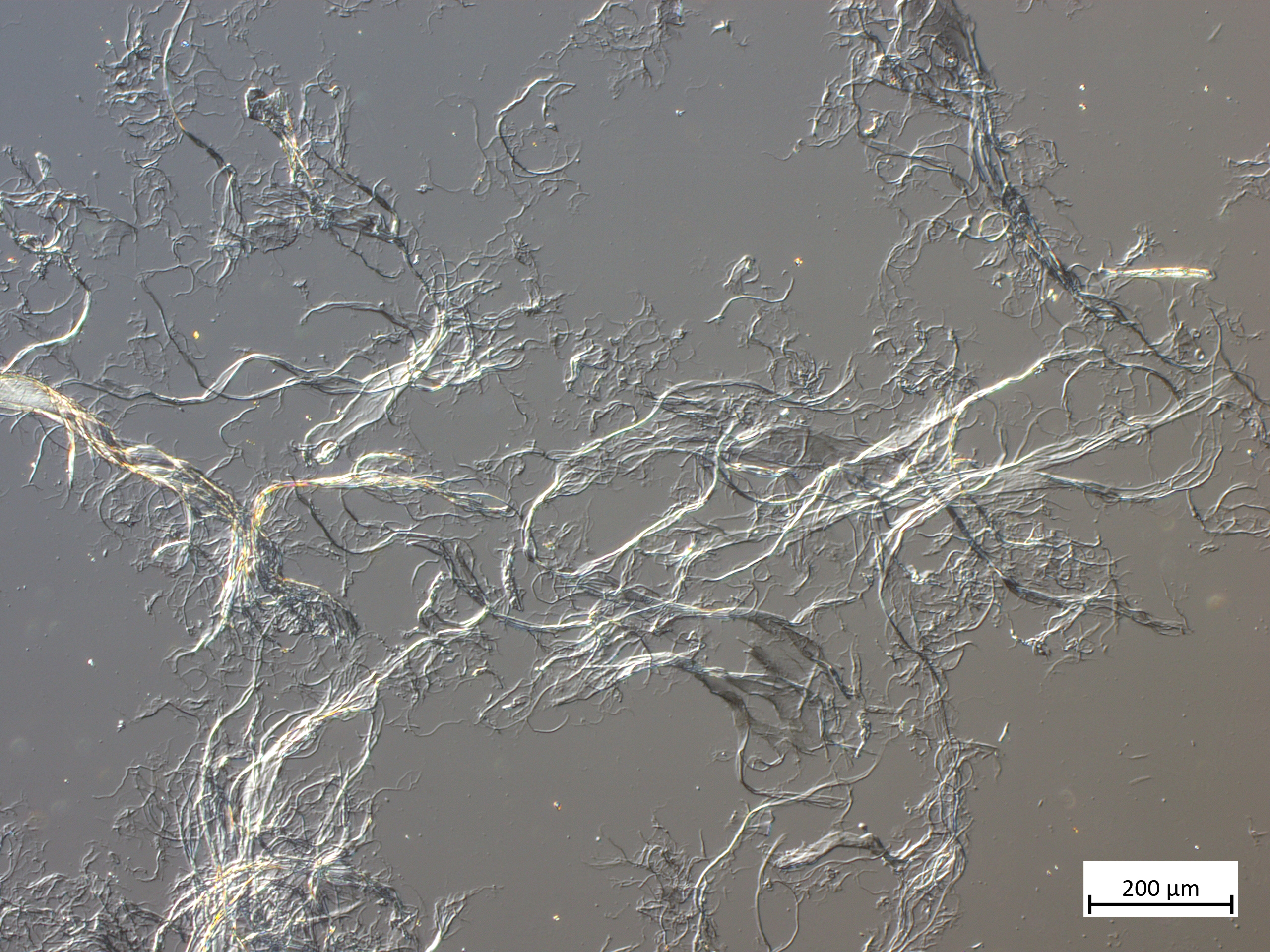
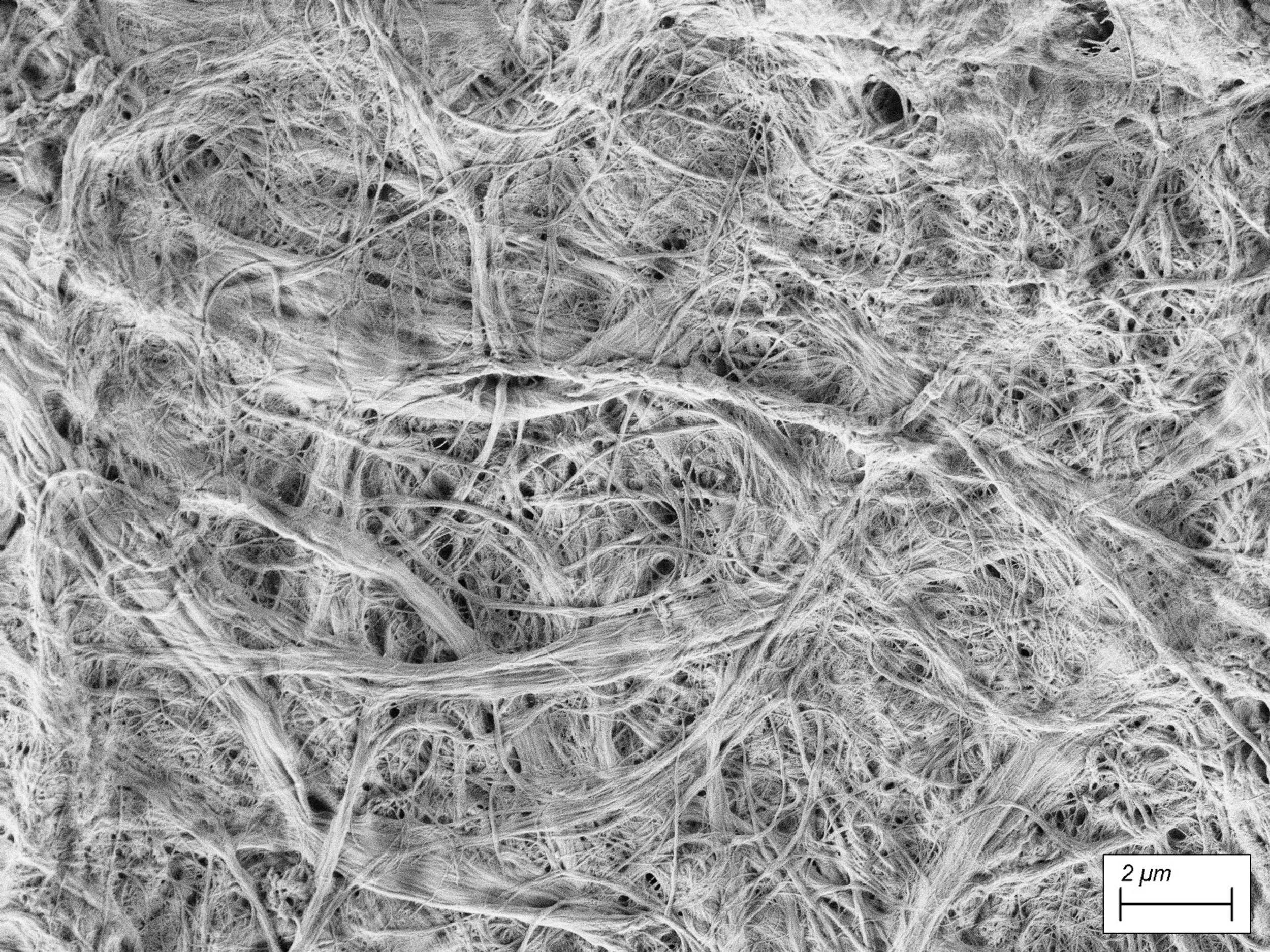
Microfibrillated Cellulose (MFC) is formed when cellulose fibres are mechanically broken down to expose and liberate these fibrils and microfibrils.
Compared to cellulose, MFC has a much higher specific surface area and particle aspect ratio, which greatly increases hydrogen bonding and network forming capability.
The FiberLean grinding process typically generates MFC with an abundance of long, thin microfibrils, which improves the bonding ability of MFC in all strength-related paper properties.These microfibrils tend to be connected together in a coarse sub-millimetre scale macrostructure, that greatly improves the inter-particle bridging ability of the MFC.
This results in a considerable improvement in retention and in bridging-sensitive paper properties such as tensile strength and porosity, compared to alternative production methods that rapidly degrade the macrostructure.